What is Ransomware?
Ransomware, a form of malicious software, functions by encrypting files and sensitive data until a specified ransom is paid. This insidious software often gains entry through various means such as phishing emails, brute force attacks, or exploiting software vulnerabilities. Once activated, it encrypts the victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible, and typically presents a ransom note demanding payment for a decryption key. Targets of ransomware attacks encompass individuals, businesses, and government entities, this can result in significant financial losses, data breaches, and operational disruptions. It’s crucial to note that paying the ransom doesn’t ensure file recovery, and there are increasing ethical as well as legal concerns surrounding the act of rewarding cybercriminals with ransom payments.
Consequences of Ransomware
Ransomware inflicts severe consequences on organizations, ranging from the loss of sensitive customer, financial, or employee data to the erosion of trust between stakeholders and the afflicted company. The compromised data not only exposes individuals to identity theft and financial fraud but also undermines the company’s reputation and credibility. Additionally, organizations are burdened with the escalated workload required to rectify vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware, diverting resources and manpower away from core operations. Moreover, the financial toll of ransomware extends beyond the potential payment made during the attack, encompassing indirect costs associated with recovery efforts and the long-term impact on business continuity.
Prominent Ransomware Groups:
-
Ryuk: Active since 2018, Ryuk has been linked to cybercriminal groups believed to operate from Russia or Eastern Europe. It gained notoriety for targeting large organizations and demanding significant ransom payments, often in the form of cryptocurrency.
-
Sodinokibi/REvil: Also known as REvil, this ransomware variant emerged in 2019 and has been associated with Russian-speaking cybercriminal groups. Sodinokibi/REvil specializes in high-profile attacks against organizations, including managed service providers (MSPs) and supply chain targets.
-
LockBit 3.0: LockBit 3.0 is a relatively newer ransomware variant that has been active since around 2021. It has been associated with various cybercriminal groups and is known for its sophisticated encryption techniques, often used in targeted attacks against organizations worldwide.
-
BlackCat: While specific information about BlackCat may be limited, it is a ransomware variant that has gained attention in recent years. It has been linked to cybercriminal groups operating primarily in Eastern Europe and has been involved in attacks targeting both individuals and organizations.
How Ransomware Works.
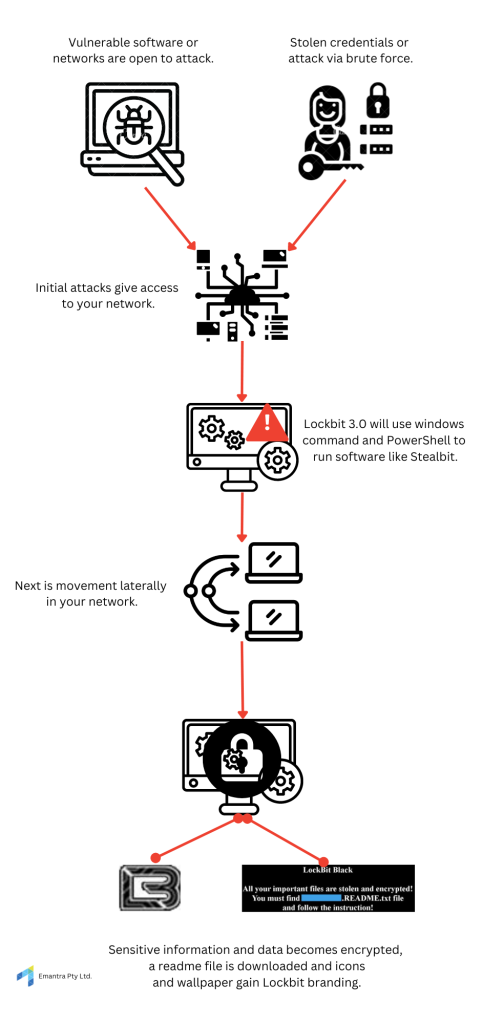
Lockbit 3.0 is a growing choice for threat actors when choosing Ransomware as a Service. A model where Ransomware can be paid for a used easily by threat actors with low technical capabilities. Vulnerable networks and software as well as credential stuffing and brute force attacks are methods that a RaaS would use to attempt to gain access to your systems. Indicators of compromise with Lockbit 3.0 in particular include distinctive changes such as replacing icons and wallpaper with its branding, an example of which is evident in the infographic provided. Compromised systems will experience the loss of access to applications on the desktop as well as the encryption of important and sensitive data and files. Additionally, LockBit 3.0 executes automatic logon on the desktop, disables privacy settings, clears Windows event logs, and employs safe mode commands, which is aimed at avoiding detection by antivirus software and increasing privileges of the software so that it may move laterally across your network. These actions collectively signify a compromised system and the potential presence of LockBit 3.0.
Mitigating Impacts of Ransomware using Backups
Mitigating the impacts of ransomware relies significantly on having robust backup systems in place. Since the primary target of ransomware attacks is data and files, ensuring frequent and comprehensive backups across the business is paramount. Backups serve as the most effective defense against the urgency and panic induced by ransomware attacks because they enable organizations to maintain access to their data even when files become encrypted and inaccessible. By preserving access to data, organizations undermine the leverage of attackers seeking ransom. However, it’s important to recognize that even with backups, there’s still a risk of sensitive data being released or sold by the attackers, irrespective of whether the ransom is paid. Nonetheless, backups remain a crucial element in mitigating the devastating effects of ransomware attacks.
What types of Backups are most effective?
-
Encrypted Backups – Employing a robust backup strategy entails more than just routine file replication; encrypting backed-up data represents an elevated security measure safeguarding sensitive information. Encrypted backup files maintain their integrity in the event of a breach, stopping unauthorized encryption or access by external entities.
-
Self-service Backups – Implementing self-service backup functionality empowers users to autonomously restore their emails and files, streamlining data retrieval processes and reducing dependency on IT personnel for restoration tasks. This should be used in conjunction with auto-backups or managed backups to ensure that files are consistently being backed up as well.
-
Air-gapped Backups- Incorporating air-gapped backups involves segregating backup systems from the primary network infrastructure, mitigating the risk of compromise in the event of server infiltration. By ensuring that backup systems remain disconnected from potentially compromised servers, the integrity of backup data is preserved, bolstering overall resilience against cyber threats.
Why Backup With Emantra?
As World Backup Day approaches on March 31st, it is important to evaluate the methods, frequency, and locations used for backing up your business’s crucial data and sensitive information. For a comprehensive understanding of your backup needs and solutions, consider reaching out to Emantra. Our services not only encompass secure cloud solutions to shield against external threats but also include Backup as a Service, eliminating the complexities of backup management. At Emantra, we store backups on immutable object storage, guaranteeing that administrators cannot overwrite or delete them. This feature is pivotal in safeguarding the integrity and security of your backups, providing peace of mind amidst evolving cybersecurity challenges.




